 J/K
J/K
Tuesday, November 3, 2009
Thursday, October 29, 2009
PYTHON in Factory
 ဒီနေ့ မနက်စောစော အလုပ်ကို ရောက်ရောက်ခြင်း လုံခြုံရေးတွေက မြွေတစ်ကောင်မိထားတယ်တဲ့ သွားကြည့်တော့ Python (စပါးအုံး) မြွေဖြစ်နေတယ် ကိုစိုးမင်း ကိုတောင် သတိရသွားတယ် :D ဒါနဲ့ ဘယ်မှာမိတာလဲဆိုတော့ Compressor တွေပေါ်မှာ အစာလာရှာတာထင်တယ်တဲ့ အဲ့ဒီမှာတွေ့တာလို့ လုံခြုံရေးတွေကပြောပါတယ်။ ကျတော်ကတော့ သတ်မစားဖို့တောင်းပန်ထားတယ်၊ သူတို့ကလဲ ဂျိုဟိုးက တိရိစ္ဆာန် ထိန်းသိမ်းရေးကို ဖုန်းဆက်ထားတယ်လို့ပြောပါတယ်၊ အထီးလား အမလားတော့ ကျတော်လဲ မခွဲတတ်ပါ၊ လောလောဆယ်တော့ သူလဲတော်တော်နာသွားတယ် လူသုံးယောက်ဝိုင်းဖမ်းရတယ်တဲ့၊ အရှည် ၉ပေကျော် လုံးပတ်ကတော့ ခန့်မှန်းခြေ ၅ လက်မကျော်မယ်ထင်တယ်၊ (ကွန်ပရက်စာတွေမှာ ငှက်တွေလာညအိပ်တယ်၊ ကြောင်တွေက ငှက်ခုတ်တယ်၊ (သူက ကြောင်ကို လာဖမ်းတာဖြစ်မယ်) ကျတော့ စိတ်ထင်ပါ :)၊ ဒီ မလေးက စက်ရုံတော်တော်များများဟာ တောတွေနဲ့နီးလို့ မျောက်၊ ဖွတ်၊ မြွေတွေ ခဏခဏ တွေ့ရ ဖမ်းမိကြတယ်၊ ဒီမနက်မှာ မြွေတွေ့တာဆိုတော့ အတိတ်ကောက်ပြီး ၄လုံးထီ သွားထိုးရဦးမယ် :D။
ဒီနေ့ မနက်စောစော အလုပ်ကို ရောက်ရောက်ခြင်း လုံခြုံရေးတွေက မြွေတစ်ကောင်မိထားတယ်တဲ့ သွားကြည့်တော့ Python (စပါးအုံး) မြွေဖြစ်နေတယ် ကိုစိုးမင်း ကိုတောင် သတိရသွားတယ် :D ဒါနဲ့ ဘယ်မှာမိတာလဲဆိုတော့ Compressor တွေပေါ်မှာ အစာလာရှာတာထင်တယ်တဲ့ အဲ့ဒီမှာတွေ့တာလို့ လုံခြုံရေးတွေကပြောပါတယ်။ ကျတော်ကတော့ သတ်မစားဖို့တောင်းပန်ထားတယ်၊ သူတို့ကလဲ ဂျိုဟိုးက တိရိစ္ဆာန် ထိန်းသိမ်းရေးကို ဖုန်းဆက်ထားတယ်လို့ပြောပါတယ်၊ အထီးလား အမလားတော့ ကျတော်လဲ မခွဲတတ်ပါ၊ လောလောဆယ်တော့ သူလဲတော်တော်နာသွားတယ် လူသုံးယောက်ဝိုင်းဖမ်းရတယ်တဲ့၊ အရှည် ၉ပေကျော် လုံးပတ်ကတော့ ခန့်မှန်းခြေ ၅ လက်မကျော်မယ်ထင်တယ်၊ (ကွန်ပရက်စာတွေမှာ ငှက်တွေလာညအိပ်တယ်၊ ကြောင်တွေက ငှက်ခုတ်တယ်၊ (သူက ကြောင်ကို လာဖမ်းတာဖြစ်မယ်) ကျတော့ စိတ်ထင်ပါ :)၊ ဒီ မလေးက စက်ရုံတော်တော်များများဟာ တောတွေနဲ့နီးလို့ မျောက်၊ ဖွတ်၊ မြွေတွေ ခဏခဏ တွေ့ရ ဖမ်းမိကြတယ်၊ ဒီမနက်မှာ မြွေတွေ့တာဆိုတော့ အတိတ်ကောက်ပြီး ၄လုံးထီ သွားထိုးရဦးမယ် :D။ Thursday, October 22, 2009
အရှက်ခွဲတဲ့ ရန်ကုန် :D
ရန်ကုန် ရန်ကုန် ကျတော့်အတွက်တော့ .....
အကြံကုန်ရင် ဆားပြန်ချက်မဲ့မြို့ပေါ့ ......
ရေလျှံ မီးပြတ် နေစရာကျပ်တဲ့ ရန်ကုန် .....
နေဝင် ညဘက် ကြက်မ စည်တဲ့ ရန်ကုန် .....
ရေမလာ ပိုက်ပျက် ရေမလောက်တဲ့ ရန်ကုန် .....
လေမဝင် အမှိုက်နဲ့ အသက်ရှူ မဝတဲ့ ရန်ကုန် .....
ဒဏ်ရာ အပြည့်နဲ့ သေတော့မယ့် ရန်ကုန် ......
ကြံရာမရ ရင်တော့ ပြန်လာရမဲ့ ရန်ကုန် ......
နင့်ကြောင့် ခက်တယ် ရန်ကုန် .......
ကယ်သူမဲ့ပြီး အရှက်ပါကွဲပေါ့ ရန်ကုန်ရယ် ....
ST-JB-Msia
Thursday, October 1, 2009
Create Cisco console cable by Yourself
1. Preparation
You should prepare the following two, as well as a Cisco and a console-terminal.
* RJ45-DSub9Pin Cable Changer (In=RJ45 Female, Out=DSub9Pin Female)
As far as I know, you can buy it at the following shops for about 500 yen:
o Jimbo-Shokai (Akiba, Tokyo, Japan)
o Plathome (Akiba, Tokyo, Japan)
* Ethernet Category-5 straight cable
Other category would be okay.
2. how to connect them
Please see the following picture. At least you must connect DSub9Pin's 2, 3, and 5 to the correct corresponding port on RJ45; others are optional.
RJ45-DSub9pin Connector Pin Layout
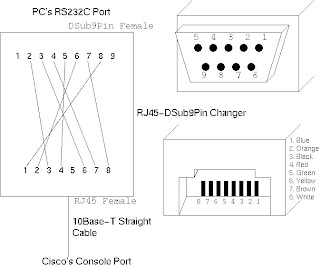 REF:->>> http://www.kame.net/~suz/cisco-cable.html
REF:->>> http://www.kame.net/~suz/cisco-cable.htmlWednesday, September 16, 2009
Hide Taskbar Tray Icon at righ corner
User Key: [HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Policies\Explorer]
System Key: [HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Policies\Explorer]
Value Name: NoTrayItemsDisplay
Data Type: REG_DWORD (DWORD Value)
Value Data: (0 = default, 1 = enable restriction) ၀ ဆိုရင် ပေါ်မယ် - ၁ ဆိုရင်ဖျောက်မယ်။
ပုံထဲက အတိုင်း နှစ်နေရာမှာ ပြင်ရေးလဲ ရတယ်၊ ပုံနဲ့ စာနဲ့ဆို ပိုလွယ်တာပေါ့။
Hate Myself
မှတ်ချက် - ဆရာ မသင် က ငပိဖုတ်တောင် ဖြောင့်ဖြောင့် မတတ်ပါ၊ ဆရာမှားရင်လဲ တစ်သံသယာ လုံးမှားနိုင်တယ်။
I am stupid man :(
Tuesday, September 15, 2009
Part 1 - Cisco Router Configuration
ဖတ်မိသလောက်လေး ပြန်ဖေါ်ပြပေးလိုက်ပါတယ်၊ http://www.firewall.cx/cisco-lab1-tutorial-1.php မှာလဲ တိုက်ရိုက်ဖတ်လို့ ရပါတယ်။
Part 1 - Cisco Router Configuration
The first part of this tutorial will help you understand how Cisco routers function and the steps required to perform basic configuration. Concepts and theory examined in our Cisco routers section are fully covered here, so you'll be able to gain some real hands-on experience.
Note that almost all configuration commands and options are the same on most Cisco routers, regardless of their model series and IOS versions. At any point, you can access the Cisco 'Help' function by using the question mark '?' symbol at the command prompt as it will provide you with a list of all supported commands along with their descriptions for the mode and the configuration section you are currently in.
Router1 Tasks:
1) Configure Hostname to "r1".
router> enable
router# configure terminal
router(config)# hostname r1
r1(config)# exit
a) Check router's IOS version, uptime, physical memory, flash memory and verify the router model as shown in the diagram. Make sure the router is configured to load nvram's startup-config when restarted or reloaded.
r1# show version
NOTE: Configuration Register (at the end of the output above) must be set to 0x2102 in order to load nvram's startup-config when restarted or reloaded. Analysis of the output from this command can be found in our site's 'Cisco Router Basics' articles.
b) List the IOS binary file located in the flash memory and verify its size of 4159154 bytes.
r1# show flash:
c)Check the router's CPU utilisation and running processors.
r1# show processes cpu
3) Set 'secret' password to "cisco". Configure VTY lines 0 to 5 (telnet) password to 'firewall'. Finally, set the 'Message of the day' (motd) banner to: "Welcome to Lab 1, Router1".
The motd banner gives a message to every person connecting to the router via telnet, console or auxiliary port.
r1# configure terminal
r1(config)# enable secret cisco
r1(config)# line vty 0 5
r1(config-line)# password firewall
r1(config-line)# exit
r1 (config)# banner motd ^
Enter TEXT message. End with the character '^'.
Welcome to Lab 1, Router1!
^
4) Disable DNS lookups to stop the router trying to resolve 'unknown commands' (typically typing mistakes) to hostnames or domains. Configure ethernet 0 interface with IP address 192.168.5.1/24, provide an interface description (locally significant) and check the interface to ensure it is not shutdown. Enter "Lan Interface" as the interface's description.
r1(config)# no ip domain-lookup
r1(config)# interface ethernet 0
r1(config-if)# ip address 192.168.5.1 255.255.255.0
r1(config-if)# description Lan Interface
r1(config-if)# no shutdown
r1(config-if)# exit
5) Copy the router's configuration running configuration (ram) to nvram and reload the router to ensure the new configuration loads automatically.
r1(config)# exit
r1# copy running-config startup-config
Destination filename [startup-config]? [hit 'enter' to accept filename]
Building configuration...
[OK]
r1# reload
Proceed with reload? [confirm] [hit 'enter' to accept]
Once the router has completed it reload cycle, you must enter the following commands to verify the previous commands exist in its configuration:
r1> enable
[Enter your secret password 'cisco']
r1# show running-config
Part 2 - Cisco Switch Configuration
The second part of the tutorial focuses on the 1900 catalyst switch. Here you'll be required to configure specific aspects while also verifing and monitoring some services. Although the 1900 series switch is considered an old and out-dated switch due to the number of units installed world-wide, we will be covering it just for this lab.
Unlike Cisco's new switches, the first generation 1900 series switches work via a menu driven prompt, making them simple and fast to work with. Our tutorial requires you to find your way through the device's menu and perform the selected functions.
Switch1 Tasks:
1) Configure the system's name to "switch1". Enter "Administrator" as the 'Contact name' and "Cisco Lab" as the 'Location' field.
Enter sequence: M , S , N --> sw1
Enter sequence: C --> Administrator
Enter sequence: L --> Cisco Lab
2) Configure the device's IP address to 192.168.5.2/24 and set the default gateway to 192.168.5.1. Optionally enter 192.168.5.1 as the 1st DNS server and 'cisco.com' as the domain name.
Enter sequence: X, N, I, I --> 192.168.5.2
Enter sequence: S --> 255.255.255.0
Enter sequence: G --> 192.168.5.1
Enter sequence: M --> 192.168.5.1
Enter sequence: D --> cisco.com
3) Change the switching mode to 'Store-and-Forward'. Decrease the Broadcast Storm 'threshold' to 100 broadcasts per second and set the switch to 'block' the offending port.
Enter sequence: X, X, S, S, 1
Enter sequence: B, T --> 100
Enter sequence: A, B
Enter sequence: X, X [Return to the main menu]
4) Set the Address aging time to 1000 seconds and set port 1 as an uplink port (Network port).
Enter sequence: S, I --> 1000
Enter sequence: P, 1
Other Tasks:
1) From the router, ping 'sw1' to verify connectivity between the two devices. Go back to your router and ping the switch from there.
r1# ping 192.168.5.2
Type escape sequence to abort.
Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 192.168.5.2, timeout is 2 seconds:
.!!!!
Success rate is 80 percent (4/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 4/5/8 ms
2) Check the amount of data transmitted and received on your router's ethernet 0 interface.
r1# show interface ethernet 0
Hint: Observe the interface's 'packets input' and 'packets output' figures.
3) Copy your router's startup-config to the local tftp server 192.168.5.100. You can provide any unique name you wish, just make sure you note it so you can retrieve it later on.
Note: The tftp server is used by all Cisco lab users, so ensure you use unique filenames (e.g username-lab1-r1) so that you don't lose your configuration file by having it overwritten by someone else.
r1# copy startup-config tftp
Address or name of remote host []? 192.168.5.100
Destination filename [r1-confg]? alan-lab1-r1-startupconfig
!!
404 bytes copied in 0.192 secs (2104 bytes/sec)
4) Backup your router's IOS image to the local tftp server 192.168.5.100.
r1# dir
Directory of flash:/
1 -rw- 4501427
16515072 bytes total (8875980 bytes free)
router1# copy flash tftp
Source filename []? c1600-y-mz.123-22.bin
Address or name of remote host []? 192.168.5.100
Destination filename [c1600-y-mz.123-22.bin]? [Hit Enter ]
!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
4501427 bytes copied in 53.944 secs (77101 bytes/sec)
5) It's now time to enable some security measures so we can limit access to our router, while at the same time protecting all passwords entered into the system.
Configure the vty ( 0 to 4) interfaces with the password 'cisco', and encrypt all passwords stored on the router:
r1# configure terminal
r1(config)# line vty 0 4
r1(config-line)# password cisco
r1(config-line)# login
r1(config-line)# exit
r1(config)# service password-encryption
NOTE: If you issue a "show running-config" command before and after the "service password-encryption" command, you'll clearly see the encryption that has taken place to secure your passwords.
6) It's now time to save our configuration to the router's NVRAM. This is done by using one simple command:
r1(config)# copy running-config startup-config
Congratulations! You have successfully completed the first tutorial of Cisco Lab No.1.
Ref:- http://www.firewall.cx/cisco-lab1-tutorial-1.php
Saturday, September 12, 2009
TCP/IP Protocol Stack Multiple Remote Denial Of Service
| Bugtraq ID: | 31545 |
| Class: | Unknown |
| CVE: | CVE-2008-4609 |
| Remote: | Yes |
| Local: | No |
| Published: | Oct 02 2008 12:00AM |
| Updated: | Sep 11 2009 11:21PM |
| Credit: | Robert E. Lee and Jack C. Lewis |
| Vulnerable: | Sun Solaris 9_x86 Sun Solaris 9 Sun Solaris 8_x86 Sun Solaris 8 Sun Solaris 10_x86 Sun Solaris 10 Sun OpenSolaris build snv_99 Sun OpenSolaris build snv_98 Sun OpenSolaris build snv_96 Sun OpenSolaris build snv_95 Sun OpenSolaris build snv_94 Sun OpenSolaris build snv_93 Sun OpenSolaris build snv_92 Sun OpenSolaris build snv_91 Sun OpenSolaris build snv_90 Sun OpenSolaris build snv_89 Sun OpenSolaris build snv_88 Sun OpenSolaris build snv_87 Sun OpenSolaris build snv_86 Sun OpenSolaris build snv_85 Sun OpenSolaris build snv_84 Sun OpenSolaris build snv_83 Sun OpenSolaris build snv_82 Sun OpenSolaris build snv_81 Sun OpenSolaris build snv_80 Sun OpenSolaris build snv_78 Sun OpenSolaris build snv_77 Sun OpenSolaris build snv_76 Sun OpenSolaris build snv_68 Sun OpenSolaris build snv_67 Sun OpenSolaris build snv_64 Sun OpenSolaris build snv_61 Sun OpenSolaris build snv_59 Sun OpenSolaris build snv_58 Sun OpenSolaris build snv_57 Sun OpenSolaris build snv_54 Sun OpenSolaris build snv_51 Sun OpenSolaris build snv_50 Sun OpenSolaris build snv_49 Sun OpenSolaris build snv_47 Sun OpenSolaris build snv_45 Sun OpenSolaris build snv_41 Sun OpenSolaris build snv_39 Sun OpenSolaris build snv_38 Sun OpenSolaris build snv_37 Sun OpenSolaris build snv_36 Sun OpenSolaris build snv_29 Sun OpenSolaris build snv_22 Sun OpenSolaris build snv_19 Sun OpenSolaris build snv_13 Sun OpenSolaris build snv_123 Sun OpenSolaris build snv_122 Sun OpenSolaris build snv_121 Sun OpenSolaris build snv_120 Sun OpenSolaris build snv_119 Sun OpenSolaris build snv_118 Sun OpenSolaris build snv_117 Sun OpenSolaris build snv_116 Sun OpenSolaris build snv_115 Sun OpenSolaris build snv_114 Sun OpenSolaris build snv_113 Sun OpenSolaris build snv_112 Sun OpenSolaris build snv_111a Sun OpenSolaris build snv_111 Sun OpenSolaris build snv_110 Sun OpenSolaris build snv_109 Sun OpenSolaris build snv_108 Sun OpenSolaris build snv_107 Sun OpenSolaris build snv_106 Sun OpenSolaris build snv_105 Sun OpenSolaris build snv_104 Sun OpenSolaris build snv_104 Sun OpenSolaris build snv_103 Sun OpenSolaris build snv_102 Sun OpenSolaris build snv_101a Sun OpenSolaris build snv_101 Sun OpenSolaris build snv_100 Sun OpenSolaris build snv_02 Sun OpenSolaris build snv_01 Sun OpenSolaris 0 Nortel Networks Self-Service WVADS 0 Nortel Networks Self-Service VoiceXML 0 Nortel Networks Self-Service Speech Server 0 Nortel Networks Self-Service Peri Workstation 0 Nortel Networks Self-Service Peri Application 0 Nortel Networks Self-Service MPS 500 0 Nortel Networks Self-Service MPS 1000 0 Nortel Networks Self-Service MPS 100 0 Nortel Networks Self-Service CCXML 0 Nortel Networks Self-Service - CCSS7 0 Nortel Networks Contact Center NCC 0 Nortel Networks Contact Center Manager Server 0 Nortel Networks Contact Center Express Nortel Networks Contact Center Administration 0 Nortel Networks Contact Center - TAPI Server 0 Nortel Networks Contact Center - Symposium Agent 0 Nortel Networks CallPilot 703t Nortel Networks CallPilot 600r Nortel Networks CallPilot 202i Nortel Networks CallPilot 201i Nortel Networks CallPilot 1005r Nortel Networks CallPilot 1002rp Microsoft Windows XP Tablet PC Edition SP3 Microsoft Windows XP Tablet PC Edition SP2 Microsoft Windows XP Professional x64 Edition SP2 Microsoft Windows XP Professional SP3 Microsoft Windows XP Professional SP2 Microsoft Windows XP Media Center Edition SP3 Microsoft Windows XP Media Center Edition SP2 Microsoft Windows XP Home SP3 Microsoft Windows XP Home SP2 Microsoft Windows Vista x64 Edition SP2 Microsoft Windows Vista x64 Edition SP1 Microsoft Windows Vista x64 Edition 0 Microsoft Windows Vista Ultimate 64-bit edition SP2 Microsoft Windows Vista Ultimate 64-bit edition SP1 Microsoft Windows Vista Ultimate 64-bit edition 0 Microsoft Windows Vista Home Premium 64-bit edition SP2 Microsoft Windows Vista Home Premium 64-bit edition SP1 Microsoft Windows Vista Home Premium 64-bit edition 0 Microsoft Windows Vista Home Basic 64-bit edition SP2 Microsoft Windows Vista Home Basic 64-bit edition SP1 Microsoft Windows Vista Home Basic 64-bit edition 0 Microsoft Windows Vista Enterprise 64-bit edition SP2 Microsoft Windows Vista Enterprise 64-bit edition SP1 Microsoft Windows Vista Enterprise 64-bit edition 0 Microsoft Windows Vista Business 64-bit edition SP2 Microsoft Windows Vista Business 64-bit edition SP1 Microsoft Windows Vista Business 64-bit edition 0 Microsoft Windows Vista Ultimate SP2 Microsoft Windows Vista Ultimate SP1 Microsoft Windows Vista Ultimate Microsoft Windows Vista SP2 Microsoft Windows Vista SP1 Microsoft Windows Vista Home Premium SP2 Microsoft Windows Vista Home Premium SP1 Microsoft Windows Vista Home Premium Microsoft Windows Vista Home Basic SP2 Microsoft Windows Vista Home Basic SP1 Microsoft Windows Vista Home Basic Microsoft Windows Vista Enterprise SP2 Microsoft Windows Vista Enterprise SP1 Microsoft Windows Vista Enterprise Microsoft Windows Vista Business SP2 Microsoft Windows Vista Business SP1 Microsoft Windows Vista Business Microsoft Windows Vista 0 Microsoft Windows Server 2008 for x64-based Systems SP2 Microsoft Windows Server 2008 for x64-based Systems 0 Microsoft Windows Server 2008 for Itanium-based Systems SP2 Microsoft Windows Server 2008 for Itanium-based Systems 0 Microsoft Windows Server 2008 for 32-bit Systems SP2 Microsoft Windows Server 2008 for 32-bit Systems 0 Microsoft Windows Server 2003 x64 SP2 Microsoft Windows Server 2003 x64 SP1 Microsoft Windows Server 2003 Web Edition SP2 Microsoft Windows Server 2003 Web Edition SP1 Microsoft Windows Server 2003 Web Edition Microsoft Windows Server 2003 Standard Edition SP2 Microsoft Windows Server 2003 Standard Edition SP1 Microsoft Windows Server 2003 Standard Edition Microsoft Windows Server 2003 Itanium SP2 Microsoft Windows Server 2003 Itanium SP1 Microsoft Windows Server 2003 Itanium 0 Microsoft Windows Server 2003 Enterprise x64 Edition SP2 Microsoft Windows Server 2003 Enterprise x64 Edition Microsoft Windows Server 2003 Enterprise Edition Itanium SP1 Beta 1 Microsoft Windows Server 2003 Enterprise Edition Itanium SP1 Microsoft Windows Server 2003 Enterprise Edition Itanium 0 Microsoft Windows Server 2003 Enterprise Edition SP1 Beta 1 Microsoft Windows Server 2003 Enterprise Edition SP1 Microsoft Windows Server 2003 Enterprise Edition Microsoft Windows Server 2003 Datacenter x64 Edition SP2 Microsoft Windows Server 2003 Datacenter x64 Edition Microsoft Windows Server 2003 Datacenter Edition Itanium SP1 Beta 1 Microsoft Windows Server 2003 Datacenter Edition Itanium SP1 Microsoft Windows Server 2003 Datacenter Edition Itanium 0 Microsoft Windows Server 2003 Datacenter Edition SP1 Microsoft Windows Server 2003 Datacenter Edition Microsoft Windows 2000 Server SP4 Microsoft Windows 2000 Server SP3 Microsoft Windows 2000 Server SP2 Microsoft Windows 2000 Server SP1 Microsoft Windows 2000 Server Microsoft Windows 2000 Professional SP4 Microsoft Windows 2000 Professional SP3 Microsoft Windows 2000 Professional SP2 Microsoft Windows 2000 Professional SP1 Microsoft Windows 2000 Datacenter Server SP4 Microsoft Windows 2000 Datacenter Server SP3 Microsoft Windows 2000 Datacenter Server SP2 Microsoft Windows 2000 Datacenter Server SP1 Microsoft Windows 2000 Datacenter Server Microsoft Windows 2000 Advanced Server SP4 Microsoft Windows 2000 Advanced Server SP3 Microsoft Windows 2000 Advanced Server SP2 Microsoft Windows 2000 Advanced Server SP1 Microsoft Windows 2000 Advanced Server IETF RFC 1123: Requirements for Internet Hosts Applicat 0 IETF RFC 1122: Requirements for Internet Hosts Communic 0 Cisco PIX/ASA 8.1 Cisco PIX/ASA 8.0 Cisco PIX/ASA 7.2 Cisco PIX/ASA 7.1 Cisco NX-OS 0 Cisco Nexus 7000 0 Cisco Nexus 5000 0 Cisco IOS XE 2.2 Cisco IOS XE 2.1 Cisco IOS 12.4YE Cisco IOS 12.4YD Cisco IOS 12.4YB Cisco IOS 12.4YA Cisco IOS 12.4XZ Cisco IOS 12.4XY Cisco IOS 12.4XW Cisco IOS 12.4XV Cisco IOS 12.4XT Cisco IOS 12.4XR Cisco IOS 12.4XQ Cisco IOS 12.4XP Cisco IOS 12.4XN Cisco IOS 12.4XM Cisco IOS 12.4XL Cisco IOS 12.4XK Cisco IOS 12.4XJ Cisco IOS 12.4XG Cisco IOS 12.4XF Cisco IOS 12.4XE Cisco IOS 12.4XD Cisco IOS 12.4XC Cisco IOS 12.4XB Cisco IOS 12.4XA Cisco IOS 12.4T Cisco IOS 12.4SW Cisco IOS 12.4MR Cisco IOS 12.4MDA Cisco IOS 12.4MD Cisco IOS 12.4JX Cisco IOS 12.4JMB Cisco IOS 12.4JMA Cisco IOS 12.4JL Cisco IOS 12.4JK Cisco IOS 12.4JDD Cisco IOS 12.4JDC Cisco IOS 12.4JDA Cisco IOS 12.4JA Cisco IOS 12.4GC Cisco IOS 12.4 Cisco IOS 12.3ZA Cisco IOS 12.3YZ Cisco IOS 12.3YX Cisco IOS 12.3YU Cisco IOS 12.3YT Cisco IOS 12.3YS Cisco IOS 12.3YQ Cisco IOS 12.3YM Cisco IOS 12.3YK Cisco IOS 12.3YJ Cisco IOS 12.3YI Cisco IOS 12.3YH Cisco IOS 12.3YG Cisco IOS 12.3YF Cisco IOS 12.3YD Cisco IOS 12.3YA Cisco IOS 12.3XZ Cisco IOS 12.3XY Cisco IOS 12.3XX Cisco IOS 12.3XW Cisco IOS 12.3XU Cisco IOS 12.3XS Cisco IOS 12.3XR Cisco IOS 12.3XQ Cisco IOS 12.3XL Cisco IOS 12.3XK Cisco IOS 12.3XJ Cisco IOS 12.3XI Cisco IOS 12.3XG Cisco IOS 12.3XF Cisco IOS 12.3XE Cisco IOS 12.3XD Cisco IOS 12.3XC Cisco IOS 12.3XB Cisco IOS 12.3XA Cisco IOS 12.3VA Cisco IOS 12.3TPC Cisco IOS 12.3T Cisco IOS 12.3JX Cisco IOS 12.3JL Cisco IOS 12.3JK Cisco IOS 12.3JED Cisco IOS 12.3JEC Cisco IOS 12.3JEB Cisco IOS 12.3JEA Cisco IOS 12.3JA Cisco IOS 12.3EU Cisco IOS 12.3BW Cisco IOS 12.3BC Cisco IOS 12.3B Cisco IOS 12.3 Cisco IOS 12.2ZYA Cisco IOS 12.2ZY Cisco IOS 12.2ZX Cisco IOS 12.2ZU Cisco IOS 12.2ZP Cisco IOS 12.2ZM Cisco IOS 12.2ZL Cisco IOS 12.2ZJ Cisco IOS 12.2ZH Cisco IOS 12.2ZG Cisco IOS 12.2ZF Cisco IOS 12.2ZE Cisco IOS 12.2ZD Cisco IOS 12.2ZC Cisco IOS 12.2ZB Cisco IOS 12.2ZA Cisco IOS 12.2YZ Cisco IOS 12.2YY Cisco IOS 12.2YX Cisco IOS 12.2YW Cisco IOS 12.2YV Cisco IOS 12.2YU Cisco IOS 12.2YT Cisco IOS 12.2YS Cisco IOS 12.2YR Cisco IOS 12.2YQ Cisco IOS 12.2YP Cisco IOS 12.2YO Cisco IOS 12.2YN Cisco IOS 12.2YM Cisco IOS 12.2YL Cisco IOS 12.2YK Cisco IOS 12.2YJ Cisco IOS 12.2YH Cisco IOS 12.2YG Cisco IOS 12.2YF Cisco IOS 12.2YE Cisco IOS 12.2YD Cisco IOS 12.2YC Cisco IOS 12.2YB Cisco IOS 12.2YA Cisco IOS 12.2XW Cisco IOS 12.2XV Cisco IOS 12.2XU Cisco IOS 12.2XT Cisco IOS 12.2XS Cisco IOS 12.2XR Cisco IOS 12.2XQ Cisco IOS 12.2XO Cisco IOS 12.2XND Cisco IOS 12.2XNC Cisco IOS 12.2XNB Cisco IOS 12.2XNA Cisco IOS 12.2XN Cisco IOS 12.2XM Cisco IOS 12.2XL Cisco IOS 12.2XK Cisco IOS 12.2XJ Cisco IOS 12.2XI Cisco IOS 12.2XH Cisco IOS 12.2XG Cisco IOS 12.2XF Cisco IOS 12.2XE Cisco IOS 12.2XD Cisco IOS 12.2XC Cisco IOS 12.2XB Cisco IOS 12.2XA Cisco IOS 12.2TPC Cisco IOS 12.2T Cisco IOS 12.2SZ Cisco IOS 12.2SY Cisco IOS 12.2SXI Cisco IOS 12.2SXH Cisco IOS 12.2SXF Cisco IOS 12.2SXE Cisco IOS 12.2SXD Cisco IOS 12.2SXB Cisco IOS 12.2SXA Cisco IOS 12.2SX Cisco IOS 12.2SW Cisco IOS 12.2SVE Cisco IOS 12.2SVD Cisco IOS 12.2SVC Cisco IOS 12.2SVA Cisco IOS 12.2SV Cisco IOS 12.2SU Cisco IOS 12.2STE Cisco IOS 12.2SRD Cisco IOS 12.2SRC Cisco IOS 12.2SRB Cisco IOS 12.2SRA Cisco IOS 12.2SQ Cisco IOS 12.2SO Cisco IOS 12.2SM Cisco IOS 12.2SL Cisco IOS 12.2SGA Cisco IOS 12.2SG Cisco IOS 12.2SEG Cisco IOS 12.2SEF Cisco IOS 12.2SEE Cisco IOS 12.2SED Cisco IOS 12.2SEC Cisco IOS 12.2SEB Cisco IOS 12.2SEA Cisco IOS 12.2SE Cisco IOS 12.2SCB Cisco IOS 12.2SCA Cisco IOS 12.2SBC Cisco IOS 12.2SB Cisco IOS 12.2S Cisco IOS 12.2MC Cisco IOS 12.2MB Cisco IOS 12.2JK Cisco IOS 12.2JA Cisco IOS 12.2IXH Cisco IOS 12.2IXG Cisco IOS 12.2IXF Cisco IOS 12.2IXE Cisco IOS 12.2IXD Cisco IOS 12.2IXC Cisco IOS 12.2IXB Cisco IOS 12.2IXA Cisco IOS 12.2IRC Cisco IOS 12.2IRB Cisco IOS 12.2IRA Cisco IOS 12.2FZ Cisco IOS 12.2FY Cisco IOS 12.2FX Cisco IOS 12.2EZ Cisco IOS 12.2EY Cisco IOS 12.2EX Cisco IOS 12.2EWA Cisco IOS 12.2EW Cisco IOS 12.2DX Cisco IOS 12.2DD Cisco IOS 12.2DA Cisco IOS 12.2CZ Cisco IOS 12.2CY Cisco IOS 12.2CX Cisco IOS 12.2BZ Cisco IOS 12.2BY Cisco IOS 12.2BX Cisco IOS 12.2BW Cisco IOS 12.2BC Cisco IOS 12.2B Cisco IOS 12.2 Cisco IOS 12.1YJ Cisco IOS 12.1YI Cisco IOS 12.1YH Cisco IOS 12.1YF Cisco IOS 12.1YE Cisco IOS 12.1YD Cisco IOS 12.1YC Cisco IOS 12.1YB Cisco IOS 12.1YA Cisco IOS 12.1XZ Cisco IOS 12.1XY Cisco IOS 12.1XX Cisco IOS 12.1XW Cisco IOS 12.1XV Cisco IOS 12.1XU Cisco IOS 12.1XT Cisco IOS 12.1XS Cisco IOS 12.1XR Cisco IOS 12.1XQ Cisco IOS 12.1XP Cisco IOS 12.1XM Cisco IOS 12.1XL Cisco IOS 12.1XJ Cisco IOS 12.1XI Cisco IOS 12.1XH Cisco IOS 12.1XG Cisco IOS 12.1XF Cisco IOS 12.1XE Cisco IOS 12.1XD Cisco IOS 12.1XC Cisco IOS 12.1XB Cisco IOS 12.1XA Cisco IOS 12.1T Cisco IOS 12.1GB Cisco IOS 12.1GA Cisco IOS 12.1EZ Cisco IOS 12.1EY Cisco IOS 12.1EX Cisco IOS 12.1EW Cisco IOS 12.1EV Cisco IOS 12.1EU Cisco IOS 12.1EO Cisco IOS 12.1EC Cisco IOS 12.1EB Cisco IOS 12.1EA Cisco IOS 12.1E Cisco IOS 12.1DC Cisco IOS 12.1DB Cisco IOS 12.1DA Cisco IOS 12.1CX Cisco IOS 12.1AZ Cisco IOS 12.1AY Cisco IOS 12.1AX Cisco IOS 12.1AA Cisco IOS 12.1 Cisco IOS 12.0XV Cisco IOS 12.0XT Cisco IOS 12.0XS Cisco IOS 12.0XR Cisco IOS 12.0XQ Cisco IOS 12.0XN Cisco IOS 12.0XM Cisco IOS 12.0XL Cisco IOS 12.0XK Cisco IOS 12.0XJ Cisco IOS 12.0XI Cisco IOS 12.0XH Cisco IOS 12.0XG Cisco IOS 12.0XF Cisco IOS 12.0XE Cisco IOS 12.0XD Cisco IOS 12.0XC Cisco IOS 12.0XB Cisco IOS 12.0XA Cisco IOS 12.0WT Cisco IOS 12.0WC Cisco IOS 12.0W Cisco IOS 12.0T Cisco IOS 12.0SZ Cisco IOS 12.0SY Cisco IOS 12.0SX Cisco IOS 12.0ST Cisco IOS 12.0SP Cisco IOS 12.0SL Cisco IOS 12.0SC Cisco IOS 12.0S Cisco IOS 12.0DC Cisco IOS 12.0DB Cisco IOS 12.0DA Cisco IOS 12.0 Cisco CatOS 8.3 GLX Cisco CatOS 8.3 (2)GLX Cisco CatOS 8.3 (1)GLX Cisco CatOS 8.2 (2) Cisco CatOS 8.2 (1) Cisco CatOS 8.2 Cisco CatOS 8.1 (3) Cisco CatOS 8.1 (2) Cisco CatOS 8.1 (1) Cisco CatOS 8.1 Cisco CatOS 7.6 (6) Cisco CatOS 7.6 (5) Cisco CatOS 7.6 (4) Cisco CatOS 7.6 (3) Cisco CatOS 7.6 (2) Cisco CatOS 7.6 (1) Cisco CatOS 7.6 Cisco CatOS 7.5 (1) Cisco CatOS 7.5 Cisco CatOS 7.4 (3) Cisco CatOS 7.4 (2) Cisco CatOS 7.4 (1) Cisco CatOS 7.4 (0.63) Cisco CatOS 7.4 (0.2)CLR Cisco CatOS 7.4 Cisco CatOS 7.3 (2) Cisco CatOS 7.3 (1) Cisco CatOS 7.3 Cisco CatOS 7.2 (2) Cisco CatOS 7.2 (1) Cisco CatOS 7.2 (0.65) Cisco CatOS 7.1 (2a) Cisco CatOS 7.1 (2) Cisco CatOS 7.1 (1a) Cisco CatOS 7.1 (1) Cisco CatOS 8.6(1) Cisco CatOS 8.5(9) Cisco CatOS 8.5(8) Cisco CatOS 8.5(6) Cisco CatOS 8.5(5.3) Cisco CatOS 8.5(5) Cisco CatOS 8.5(4) Cisco CatOS 8.5(3) Cisco CatOS 8.5(2) Cisco CatOS 8.5(1) Cisco CatOS 8.4(9)GLX Cisco CatOS 8.4(6)GLX Cisco CatOS 8.4(5) Cisco CatOS 8.4(2a) Cisco CatOS 8.4(11)GLX Cisco CatOS 8.4(10)GLX Cisco CatOS 8.3(7) Cisco CatOS 8.3(4) Cisco CatOS 8.1(3) Cisco CatOS 7.6(8) Cisco CatOS 7.6(7) Cisco CatOS 7.6(20) Cisco CatOS 7.6(19.2) Cisco CatOS 7.6(19) Cisco CatOS 7.6(18) Cisco CatOS 7.6(17) Cisco CatOS 7.6(16) Cisco CatOS 7.6(15) Cisco CatOS 7.6(12) Cisco CatOS 7.6(10) 3DM Software Disk Management Software SP2 3DM Software Disk Management Software SP1 |
| | |
| Not Vulnerable: | Cisco PIX/ASA 8.1(2.3) Cisco PIX/ASA 8.0(4.9) Cisco PIX/ASA 7.2(4.18) Cisco PIX/ASA 7.1(2.79) Cisco NX-OS 4.1(4) Cisco NX-OS 4.0(1a)N2(1) Cisco IOS XE 2.2.3 Cisco IOS 12.4(9)XG4 Cisco IOS 12.4(6)XE4 Cisco IOS 12.4(5)T5e Cisco IOS 12.4(4)XD12 Cisco IOS 12.4(3)JL1 Cisco IOS 12.4(3)JK4 Cisco IOS 12.4(25) Cisco IOS 12.4(24)T Cisco IOS 12.4(24)GC1 Cisco IOS 12.4(23a) Cisco IOS 12.4(22)YE Cisco IOS 12.4(22)YD Cisco IOS 12.4(22)YB Cisco IOS 12.4(22)XR Cisco IOS 12.4(22)T1 Cisco IOS 12.4(22)MDA Cisco IOS 12.4(22)MD Cisco IOS 12.4(22)GC1 Cisco IOS 12.4(21a)JX Cisco IOS 12.4(21a)JA Cisco IOS 12.4(20)YA2 Cisco IOS 12.4(20)T2 Cisco IOS 12.4(19)MR2 Cisco IOS 12.4(18d) Cisco IOS 12.4(16b)JA1 Cisco IOS 12.4(15)XZ2 Cisco IOS 12.4(15)XY4 Cisco IOS 12.4(15)XR4 Cisco IOS 12.4(15)XQ2 Cisco IOS 12.4(15)XM3 Cisco IOS 12.4(15)XL4 Cisco IOS 12.4(15)T6a Cisco IOS 12.4(15)SW3 Cisco IOS 12.4(15)MD2 Cisco IOS 12.4(11)XW10 Cisco IOS 12.4(11)MD7 Cisco IOS 12.4(10b)JDD Cisco IOS 12.4(10b)JDC Cisco IOS 12.4(10b)JDA3 Cisco IOS 12.3(8)JEC3 Cisco IOS 12.3(23)BC6 Cisco IOS 12.3(21a)BC9 Cisco IOS 12.3(14)YX14 Cisco IOS 12.3(14)YM13 Cisco IOS 12.2(52)XO Cisco IOS 12.2(50)SG Cisco IOS 12.2(50)SE Cisco IOS 12.2(46)SE2 Cisco IOS 12.2(44)SQ2 Cisco IOS 12.2(44)SE5 Cisco IOS 12.2(44)EY Cisco IOS 12.2(34)SB2 Cisco IOS 12.2(33)SXI1 Cisco IOS 12.2(33)SXH5 Cisco IOS 12.2(33)SRD1 Cisco IOS 12.2(33)SRC3 Cisco IOS 12.2(33)SRB5a Cisco IOS 12.2(33)SCB1 Cisco IOS 12.2(33)SB1b Cisco IOS 12.2(33)IRC Cisco IOS 12.2(31)SGA9 Cisco IOS 12.2(31)SB14 Cisco IOS 12.2(29)SVE1 Cisco IOS 12.2(29)SM5 Cisco IOS 12.2(28)SB13 Cisco IOS 12.2(18)ZYA1 Cisco IOS 12.2(18)SXF16 Cisco IOS 12.2(18)IXH Cisco IOS 12.2(15)MC2m Cisco IOS 12.2(12)DA14 Cisco IOS 12.1(22)EA13 Cisco IOS 12.0(33)S3 Cisco IOS 12.0(32)SY9a Cisco IOS 12.0(32)SY8 Cisco IOS 12.0(32)SY10 Cisco IOS 12.0(32)S12 Cisco IOS 12.0(30)SZ10 Cisco CatOS 8.7(2a) Cisco CatOS 7.6(24a) Ref:- http://www.securityfocus.com/bid/31545 |
Thursday, September 10, 2009
About MAC Address
သိသလောက် ရေးထားသည် ။ MAC address ကို ipconfig /all ဒါမှမဟုတ် getmac ဆိုတဲ့ command နှစ်ခုသုံး ပြီး ရှာလို့ရပါတယ် တခြား နည်းလမ်းတွေလဲ ရှိမှာပါ။ အဓိက မှတ်မိသလောက်ကတော့ ပထမ HEX ခြောက်လုံးက Vendor Companyကို ကိုယ်စားပြုပါတယ်။ နောက်ခြောက်လုံးကတော့ ကဒ်တွေရဲ့ serial အစဉ်လိုက်ဖြစ်ပါတယ်။ ရှေ့ဆုံးခြောက်လုံး ဟာ IEEE ကခွဲဝေသတ်မှတ်ပေးထားတာပါ၊ ဒီရှေ့ခြောက်လုံးကို ကြည့်ပြီးတော့ ဘယ် Vendor က ထုတ်လဲ ဆိုတာကို စစ်လို့ရပါတယ်၊ ရှေ့ဆုံး HEX ခြောက်လုံးကို copy ကူးပါ ပြီးရင် ဒီကို သွားပါ၊ Find Manufacture မှာထည့်ပြီး နှိပ်လိုက်ရင် အောက်က Result မှာ ထုတ်တဲ့ Vendor ကိုပြပါလိမ့်မယ်၊
Media Access Control (MAC) addresses are talked about in various sections on the site, such as the OSI-Layer 2, Multicast, Broadcast and Unicast. We are going to analyst them in depth here so we can get a firm understanding of them since they are part of the fundamentals of networking.
MAC addresses are physical addresses, unlike IP addresses which are logical addresses. Logical addresses require you to load special drivers and protocols in order to be able to configure your network card/computer with an IP Address, whereas a MAC address doesn't require any drivers whatsoever. The reason for this is that the MAC address is actually "burnt-in" into your network card's memory chipset.
The Reason for MAC
Each computer on a network needs to be identified in some way. If you're thinking of IP addresses, then you're correct to some extent, because an IP address does identify one unique machine on a network, but that is not enough. Got you mixed up?
Check the diagram and explanation below to see why :
You see, the IP address of a machine exists on the 3rd Layer of the OSI model and, when a packet reaches the computer, it will travel from Layer 1 upwards, so we need to be able to identify the computer before Layer 3.
This is where the MAC address - Layer 2 comes into the picture. All machines on a network will listen for packets that have their MAC address in the destination field of the packet (they also listen for broadcasts and other stuff, but that's analysed in other sections). The Physical Layer understands the electrical signals on the network and creates the frame which gets passed to the Datalink layer. If the packet is destined for the computer then the MAC address in the destination field of the packet will match, so it will accept it and pass it onto the Layer above (3) which, in turn, will check the network address of the packet (IP Address), to make sure it matches with the network address to which the computer has been configured.
Looking at a MAC
Let's now have a look at a MAC address and see what it looks like! I have taken my workstations MAC address as an example:
When looking at a MAC address, you will always see it in HEX format. It is very rare that a MAC address is represented in Binary format because it is simply tooooo long as we will see futher on.
When a vendor, e.g Intel, creates network cards, they don't just give them any MAC address they like, this would create a big confusion in identifying who created this network card and could possibly result in clashing with another MAC address from another vendor e.g D-link, who happened to choose the same MAC address for one of their network cards !
To make sure problems like this are not experienced, the IEEE group split the MAC address in half, and used the first half to identify the vendor, and the second half is for the vendor to allocate as serial numbers:
The Vendor code is specified by RFC - 1700. You might find a particular vendor having more than just one code; this is because of the wide range of products they might have. They just apply for more, as they need !
Keep in mind that even tho the MAC address is "burnt-in" to the network card's memory, some vendors will allow you to download special programs to change the second half of the MAC address on the card. This is because the vendors actually reuse the same MAC addresses for their network cards because they create so many that they run out of numbers ! But at the same time, the chances of you buying two network cards which have the same MAC address are so small that it's almost impossible !
Let's start talking bits and bytes!
Now that we know what a MAC address looks like, we need to start analysing it. A MAC address of any network card is always the same length, that is, 6 Bytes long or 48 Bits long. If you're scratching your head wondering where these figures came from, then just have a look at the picture below which makes it a bit easier to understand:
So that completes the discussion regarding MAC Addresses! I hope you have understood it all because it's very important so you can expand your knowledge and truly understand what happens in a network !
Ref: - http://www.firewall.cx/mac_addresses.php
Wednesday, September 9, 2009
Tweak XP (Note1)
+ Click on START - RUN and type the following (follwed by ENTER):
+ rundll32.exe keymgr.dll,KRShowKeyMgr
>>> Changing ANY user password without having to know the existing password
+ This tweak gives a user the opportunity to use it for good or bad. It enables the user to re-password any account without having to know the existing password and also shows you every account that exists on the machine (even the ones that are hidden). This is a good tool to use if you forgot a password to say your administrator account and you needed to be logged into the admin account for any reason.
To view all of the user accounts:
1) While logged onto the computer, click on Start>Run>and type in CMD.
2) From the command prompt window, type in net users. This will show you every account that is made onto the computer whether it is hidden or not.
-----------------------------------------------------------------
To change an account password:
1) While logged onto the computer to an account that has administrative rights, click on Start>Run>and type in CMD.
2) Type in net user then the name of the account then * and press enter. heres an example: net user administrator * or net user "Joe Smith" * . Put the name in quotes if it contains spaces.
3) From there it should ask for a new password. Type in your new password (type very carefully - the command window won't display what you type) and once more to confirm it. If you get the message that the command succeeded successfully you're all set!!Tuesday, September 8, 2009
Crack Exe
#မှတ်ချက်။ ။ *ကျတော်သည် Programming နှင့် Hacking Skill လုံးဝ မရှိပါ၊ တတ်လဲမတတ်ပါ။ ကျတော် ထင်မြင်မှု မှားကောင်း မှား နိုင်ပါတယ်။ ကဲကြည့် လိုက်ကြပါဦး >>>
VBA Macro to remove DisableCMD CMD.EXE restriction from Max Moser on Vimeo.
exe2vba_max howto from Max Moser on Vimeo.



